
SNMP managers send protocol data units (PDUs) called SNMP GET requests to all the devices across the network with SNMP agents installed. SNMP enables the network to gather information about a variety of device activity and performance metrics, including the number of bytes, errors, and packets sent and received by a router the speed of the network connection between devices and the number of hits received by a web server. Network traffic naturally fluctuates over the course of the average day as end users perform their required tasks, which can include data transfers, downloads, and several other activities using network bandwidth.
#Snmp trap receiver read update
The device agents retain their own copy of the MIB file, which they continue to update between poll requests, ensuring the information each device returns to the management system is accurate and up-to-date. The device agents respond to the central manager’s requests by sending back an MIB-compliant file. Periodically, the SNMP central manager will poll all the device agents across the network with information requests. Data displays may be easy-to-read user dashboards with graphic representations for quick insights about network-wide device performance.
#Snmp trap receiver read software
This network management software will likely include an interface capable of interpreting MIB files and displaying the data they gather from device agents.
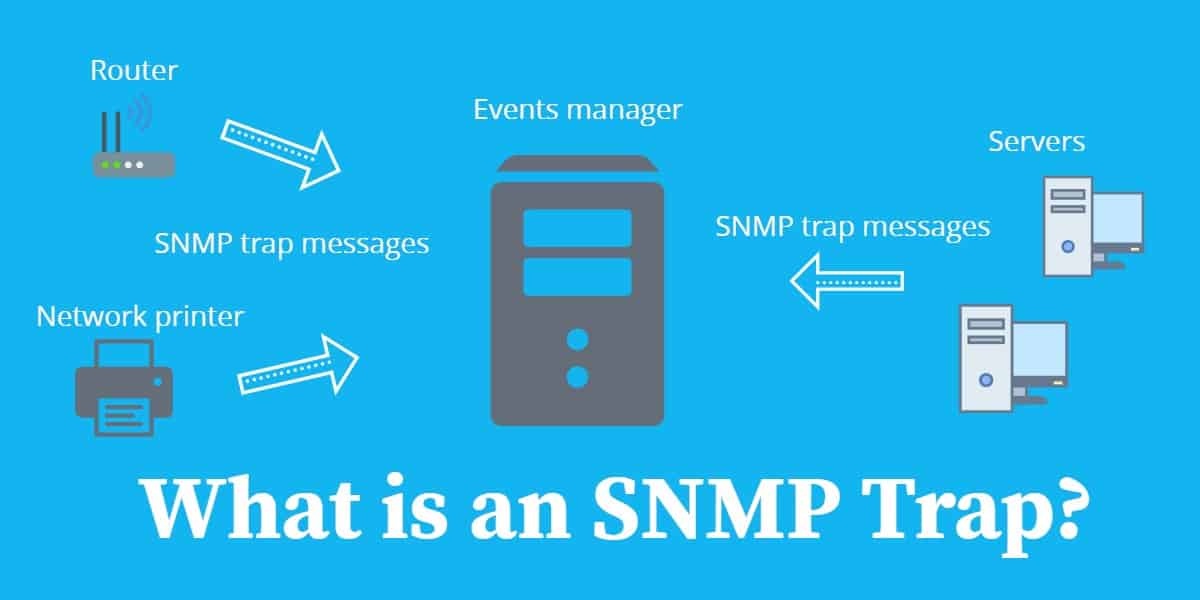
However, installing a network monitoring system on a workstation will likely make use of SNMP and will designate it as the SNMP manager for the various SNMP-agented devices across the network. The central manager isn’t usually included in the operating system of many workstations. The majority of network devices come with preinstalled SNMP agents, which may need to be activated before SNMP can be employed across the network. There are three primary elements to SNMP: a central manager, device agents, and management information bases (or MIBs). SNMP enables numerous functions network management tools rely on, including device identification, network performance monitoring, and real-time determination of the status of network devices. SNMP stands for Simple Network Management Protocol, which is a widely used method of sharing information between devices on a network, regardless of differences in device hardware or the software they’re running. The function of SNMP agents can be interrupted when a device’s network card breaks, but the next time the SNMP manager sweeps the network for responses, the emergency condition or event will be detected. This causes the SNMP agents monitoring the devices to stop operating, preventing them from contacting the SNMP manager. Fatal errors, for instance, cause devices to stop functioning. On the other hand, some serious events and conditions may not result in trap messages. For instance, SNMP agents installed on printers can treat a low toner cartridge as a trap condition and will notify the SNMP manager when the printer detects supplies are beginning to run low. Traps are the most convenient way to get notifications regarding network events and can be set for conditions with varying degrees of severity. This makes them valuable-if not necessary-assets for network monitoring.
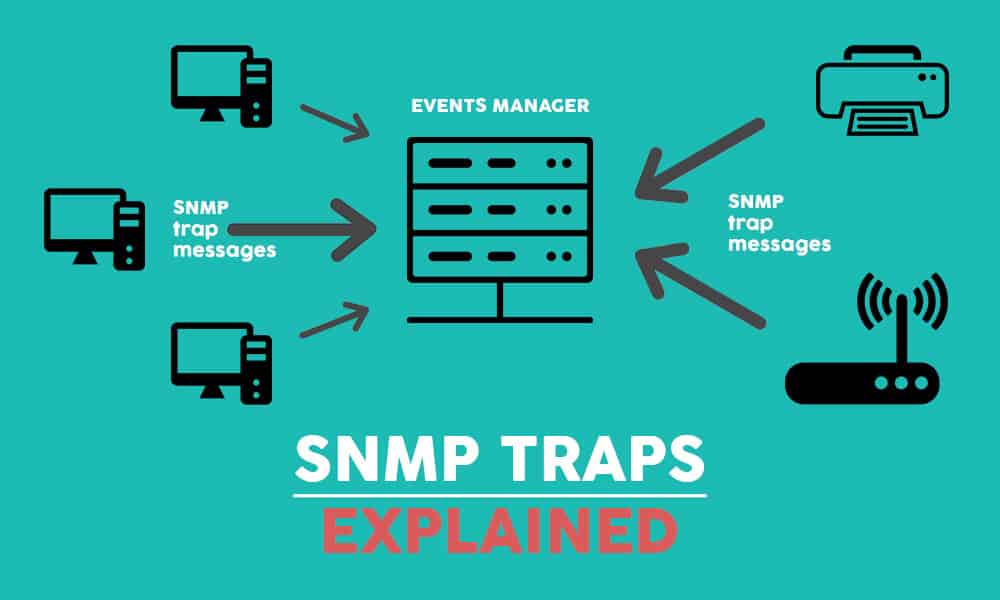
SNMP traps are unique because they’re the only notification method SNMP agents can initiate. These emergency notifications are known as SNMP traps. However, if an agent detects certain emergency conditions or events, it’ll send a warning notification to the manager without a prior request for data. Normal SNMP operations designate that device agents take passive roles, which means they’ll only send SNMP messages if the SNMP manager sends a request. SNMP traps are the most commonly used kind of SNMP message.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
